Tech Evolution for Applications
The world of application development has evolved dramatically over the past few decades. What started with simple, monolithic applications has transformed into a complex ecosystem driven by cloud computing, microservices, artificial intelligence (AI), and automation. As businesses increasingly rely on software to drive innovation and stay competitive, understanding the evolution of application development technologies becomes essential. In this blog, we’ll explore the key milestones in tech evolution and their impact on modern application development.
1. The Early Days: Monolithic Applications
In the early stages of software development, applications were primarily monolithic in structure. A monolithic application is a single, unified codebase that includes all aspects of the system, from user interfaces to business logic and data storage. While monolithic architecture was simpler to develop and deploy initially, it became difficult to maintain and scale over time as applications grew in size and complexity.
Challenges of Monolithic Applications:
- Scalability: Scaling a monolithic system meant duplicating the entire application, even if only certain parts required more resources.
- Flexibility: Any change to one part of the system could potentially affect the whole application, making updates risky and time-consuming.
- Longer development cycles: With a large, single codebase, collaboration among different teams became harder.
2. The Rise of Microservices Architecture
As businesses required more flexibility, scalability, and faster time-to-market, microservices architecture began to take shape. Microservices break down an application into smaller, self-contained services, each handling a specific task or business function. These services are independently deployable, scalable, and manageable.
Benefits of Microservices:
- Independent Scaling: Individual services can be scaled independently, ensuring optimal resource usage.
- Faster Development: Teams can work on different services without waiting for other teams, leading to faster development cycles.
- Fault Isolation: Since each service is isolated, a failure in one service doesn't bring down the entire system.
However, with the flexibility of microservices comes the complexity of managing many independently deployed services. This is where tools like Docker (for containerization) and Kubernetes (for orchestration) became essential.
3. Cloud Computing: Changing the Infrastructure Game
The shift to cloud computing transformed the way applications were built and deployed. Cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud made it easier for businesses to scale their applications without investing in expensive physical infrastructure. Cloud platforms also provided access to a wide array of services, such as databases, machine learning tools, and storage solutions, making it easier for developers to focus on building applications rather than managing servers.
Cloud Computing Benefits
- Cost Efficiency: Pay only for the resources you use, with the ability to scale up or down depending on demand.
- Elasticity: Applications can automatically scale based on traffic, ensuring optimal performance.
- Accessibility: Cloud platforms enable teams to work collaboratively from anywhere, increasing flexibility.
With cloud computing, businesses could move beyond the limitations of on-premise infrastructure, ensuring rapid development and deployment.
4. Serverless Computing: Further Simplifying Application Development
Serverless computing took cloud computing a step further. Serverless doesn’t mean there are no servers involved; rather, it means developers don’t have to manage or provision servers themselves. Platforms like AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions, and Azure Functions allow developers to write functions that automatically scale based on demand.
Key Advantages of Serverless
- Reduced Operational Overhead: Developers focus solely on writing the application code without worrying about infrastructure management.
- Scalability: Serverless functions automatically scale up or down depending on the volume of requests.
- Cost-Efficiency: With a pay-as-you-go model, businesses only pay for the actual execution time of functions.
Serverless computing has significantly reduced the complexity of building and deploying applications, making it a popular choice for modern applications that require agility and scalability.
5. The Rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are now integral to the development of modern applications. From recommendation systems and chatbots to predictive analytics and personalized experiences, AI and ML have changed the way applications interact with users and process data.
Examples of AI-Driven Applications
- Recommendation Engines: E-commerce platforms like Amazon and streaming services like Netflix use AI to recommend products or content based on user preferences.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): AI-powered virtual assistants, like Siri and Alexa, use NLP to understand and respond to voice commands.
- Predictive Analytics: Applications in finance and healthcare use ML models to predict future trends or diagnose diseases.
AI and ML have elevated applications to a level of intelligence that can dynamically adapt to user behavior and predict outcomes with greater accuracy, ultimately providing users with more personalized and relevant experiences.
6. DevOps and Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery (CI/CD)
In response to the demand for faster delivery of software, DevOps practices and CI/CD pipelines emerged. DevOps emphasizes collaboration between development and operations teams to automate and streamline the deployment process, ensuring faster and more reliable releases.
Key Components of DevOps and CI/CD
- Continuous Integration (CI): Developers frequently commit code to a shared repository, where automated testing ensures new changes don’t break existing functionality.
- Continuous Delivery (CD): Code is automatically deployed to production or staging environments, reducing the time from development to deployment.
- Automation: Automating manual tasks such as testing, deployment, and monitoring leads to more efficient development workflows.
DevOps and CI/CD have become essential for modern software development, enabling rapid iteration, reducing errors, and improving collaboration across teams.
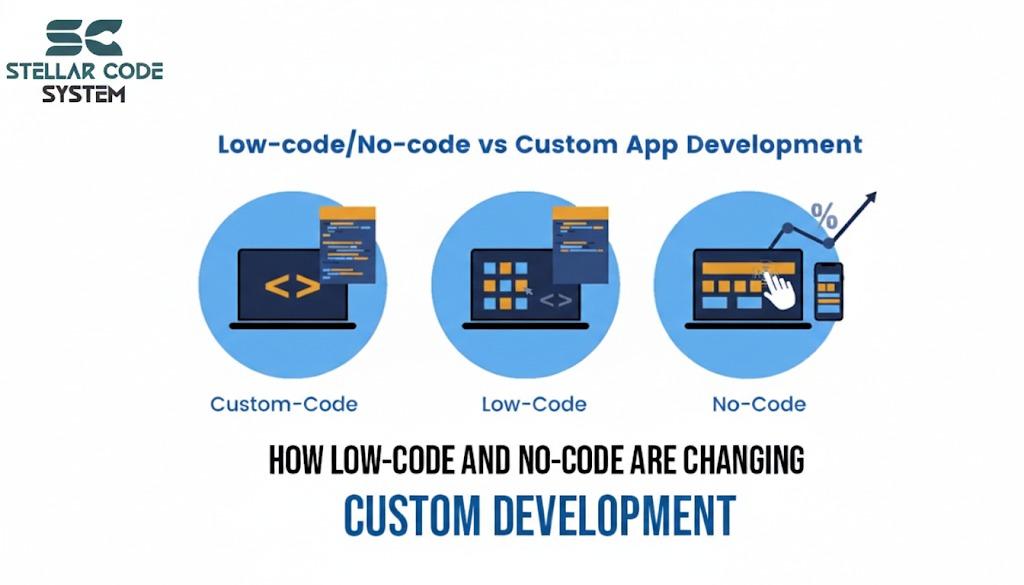
7. The Future of Application Development: Low-Code/No-Code and Edge Computing
Looking to the future, two major trends are poised to further transform application development: Low-Code/No-Code Development and Edge Computing.
Emerging Trends
- Low-Code/No-Code Development: These platforms allow non-technical users to build applications by using visual interfaces instead of writing code. This democratizes app development and enables businesses to quickly create solutions.
- Edge Computing: With edge computing, data is processed closer to the source (e.g., IoT devices), reducing latency and improving real-time processing for applications that require immediate feedback.
Both trends are expected to simplify development processes, make applications more responsive, and increase the accessibility of technology for non-developers.
8. Conclusion
From monolithic systems to microservices, cloud computing to AI, the tech evolution for applications has been nothing short of transformative. With each advancement, application development has become faster, more scalable, and more intelligent. As we look to the future, new trends like low-code platforms and edge computing will continue to shape how applications are built and used. By embracing these innovations, developers can build applications that are not only more efficient but also better aligned with the needs of modern businesses and users.
About the Author
Paras Dabhi
VerifiedFull-Stack Developer (Python/Django, React, Node.js) · Stellar Code System
Hi, I’m Paras Dabhi. I build scalable web applications and SaaS products with Django REST, React/Next.js, and Node.js. I focus on clean architecture, performance, and production-ready delivery with modern UI/UX.

Paras Dabhi
Stellar Code System
Building scalable CRM & SaaS products
Clean architecture · Performance · UI/UX