Mobile App Development Trends You Can’t Ignore in 2026

If you had asked me in 2021 how most mobile apps would be built in 2026, I would have said: “by developers, writing thousands of lines of custom code, over several months.”
That answer is already outdated.
Today, I regularly work with founders and business teams who ship real, revenue-generating apps without traditional development teams. Some have never written a line of code.
Yet they are launching MVPs, collecting payments, testing ideas, and iterating faster than many funded startups I consult for.
2026 is not about “cool tech.” It’s about who can build, how fast they can validate, and how cheaply they can reach the market.
This guide breaks down the mobile app development trends that actually change outcomes — not hype — and shows you how to use them to build smarter, faster, and with lower risk.
The Real Shift: App Building Is Becoming Product-Led, Not Developer-Led

The biggest change I see on the ground is this: Apps are no longer gated by engineering teams.
They are gated by clarity of problem and speed of execution.
Low-code platforms, AI builders, and mature cross-platform frameworks have moved from “experiments” to “production infrastructure.” Enterprises are already using them. Startups are building on them. And non-technical founders are quietly shipping while others are still “planning.”
In practice, this means:
Validation now matters more than technical skills
Proving that users want your app is more important than coding expertise.
Early testing reduces risk and guides feature development.
Speed beats perfect architecture
Launching quickly allows you to learn and iterate faster than waiting for flawless systems.
Fast MVPs capture opportunities and feedback early.
Builders who can define problems clearly outperform those who can only write code
Understanding the user’s pain and designing solutions strategically creates more successful apps.
Coding alone doesn’t guarantee adoption or value.
From a business perspective, this is the most important mobile app development trend of 2026.
Trend 1: AI-First App Development (Not “Apps With AI”)

Most articles talk about “adding AI features.”
That’s old thinking.
The real transformation is that AI is becoming the development layer itself.
In my recent client projects, AI is now used to:
Generate full app structures (frontend + backend)
AI tools can now create complete app foundations, including user interfaces, server logic, and databases.
This removes the need to manually set up complex project structures.
Create database models from plain English
You can describe your data needs in simple language, and the system builds the database tables and relationships automatically.
This reduces errors and speeds up development.
Build authentication and admin systems
Login, signup, roles, and admin dashboards can be generated instantly.
This ensures security and control without custom development.
Debug broken features by scanning logs and files
AI can read error logs and project files to identify issues and suggest fixes.
This cuts down troubleshooting time dramatically.
Integrate third-party APIs in minutes
Payment, messaging, maps, and email services can be connected quickly using AI-assisted integrations.
This allows apps to become fully functional much faster.
Instead of hiring separate UI, backend, and QA resources, founders are describing what they want built and supervising the output.
What this looks like in real projects
Instead of hiring separate UI, backend, and QA resources, founders are describing what they want built and supervising the output.
A local services startup I advised last quarter built their first working customer app in 18 days. Normally, this would have taken 3–4 months.
They used AI builders to:
Generate their React-based mobile interface
AI tools can automatically build responsive mobile screens using React frameworks.
This speeds up UI creation and ensures modern, scalable design standards.
Auto-create their booking and user tables
The system generates structured database tables for users, bookings, and records.
This allows apps to store, manage, and retrieve data reliably from day one.
Set up login, OTP, and admin access
Secure authentication systems are created with email, phone, and OTP verification.
Admin panels allow controlled access to manage users and content.
Connect payments and email notifications
Payment gateways and automated emails are integrated into the app flow.
This enables real transactions, confirmations, and user communication instantly.
The founder’s role wasn’t “coding.” It was product thinking, testing flows, and talking to users.
Buyer problem this solves
“I can’t afford a full dev team.”
Modern AI and low-code tools reduce the need for large development teams.
Founders can now launch functional apps with minimal upfront investment.
“My idea is good but I don’t know where to start.”
AI-powered platforms guide founders from concept to working product.
They turn plain ideas into structured app flows and features quickly.
“Agencies are quoting 6 months and huge budgets.”
Traditional development is slow and expensive due to large teams and long cycles.
New tools enable faster launches in weeks instead of months.
AI-first development directly attacks all three.
How to use this trend correctly
Step 1: Define outcomes, not features
Focus on the result users should achieve, not the type of app.
Clear outcomes help AI tools build useful, business-driven solutions instead of generic products.
Step 2: Let AI scaffold the full system
Use platforms that create the complete app foundation at once.
This ensures your frontend, backend, database, and authentication work together from the start.
Step 3: Act as product owner, not coder
Your role is to test user journeys, improve usability, and remove confusion.
Success comes from decision-making, not writing code.
Step 4: Lock scope aggressively
Limit your app to one core problem, one main user, and one primary action.
Tight scope reduces cost, speeds launch, and improves product clarity.
Trend 2: On-Device Intelligence and the New Privacy Advantage

Where your app processes data is now a competitive decision.
We are seeing a strong move toward on-device AI and edge processing, driven by:
User privacy awareness
Users are more conscious than ever about how their data is collected and stored.
Apps that protect privacy and minimize data sharing build stronger trust.
Regulatory pressure
Governments are tightening data protection and AI usage laws worldwide.
Apps must now design compliance into products from the beginning.
Performance expectations
Users expect apps to be fast, responsive, and work even with poor internet connections.
Slow or unreliable apps are quickly abandoned.
Rising cloud AI costs
Cloud-based AI processing is becoming increasingly expensive as usage scales.
Builders must optimize where and how AI is used to control long-term costs.
Apps that rely entirely on the cloud feel slower, cost more to scale, and create trust barriers.
What’s changing in practice
Modern mobile devices can now:
Summarize content locally
Apps can now generate summaries directly on the user’s device without sending data to servers.
This improves privacy, speed, and offline usability.
Process images and speech offline
Modern devices can analyze photos and voice inputs without internet access.
This reduces delays, protects user data, and improves reliability.
Personalize experiences without server calls
User preferences and behavior can be handled directly on the device.
This enables faster personalization and limits data transfer to the cloud.
Run intelligent automations without latency
Smart actions can happen instantly without waiting for server responses.
This makes apps feel smoother, faster, and more premium.
This opens the door to a new positioning advantage.
Business impact I see
Apps that can say:
“Your data never leaves your phone.”
convert better in finance, health-adjacent, education, and productivity niches.
They also:
Work during poor connectivity
Apps can continue functioning even with weak or no internet access.
This improves user reliability in travel, rural, and low-network situations.
Reduce backend infrastructure costs
Local processing lowers dependence on cloud servers and paid APIs.
This significantly cuts long-term operational expenses.
Feel noticeably faster to users
On-device processing removes network delays from core actions.
The result is smoother interactions and better overall user experience.
Example use cases
- Expense trackers that categorize receipts offline
- Fitness apps that analyze movement without uploads
- Language apps that translate speech without servers
- Journaling apps that never store personal entries remotely
How builders should respond
Design features that still work without internet
Build core functions that operate even when connectivity is weak or unavailable.
This improves reliability, usability, and customer trust.
Keep sensitive processing on the device when possible
Handle personal and critical data locally instead of sending it to servers.
This strengthens privacy, security, and regulatory compliance.
Market privacy as a product feature, not a policy page
Highlight data protection as a key benefit in your messaging.
Users respond more to visible privacy advantages than hidden legal statements.
In crowded app categories, trust is now a growth lever.
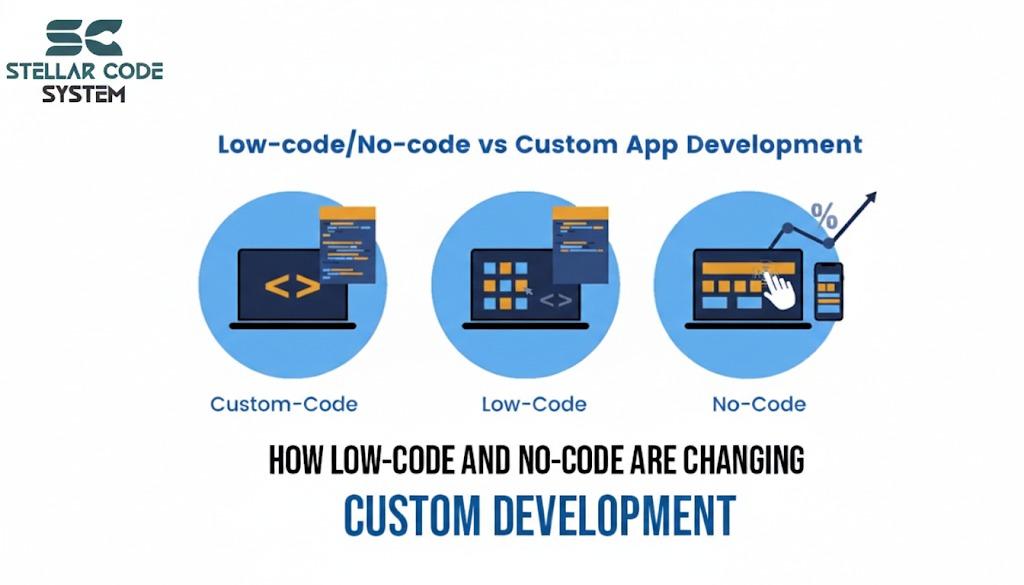
Trend 3: Cross-Platform Tech Has Finally Grown Up

For years, founders had to choose between:
Native apps (expensive, slow, duplicated effort)
Building separate apps for iOS and Android requires larger teams and longer timelines.
The same features must be developed and maintained twice.
Cross-platform apps (cheaper, but risky and unstable)
Earlier cross-platform solutions reduced costs but often suffered from performance and stability issues.
Many businesses hesitated due to long-term reliability concerns.
That tradeoff is largely gone.
Flutter, React Native, and Kotlin Multiplatform are now powering serious production systems.
The difference this creates is subtle but massive.
Why this matters even if you don’t code
Most AI and no-code platforms now generate apps on top of these stable frameworks.
That means:
Better performance
Modern cross-platform frameworks now deliver near-native speed and smooth UI.
This results in faster apps and improved user satisfaction.
Easier hiring later
Widely adopted frameworks make it simpler to find skilled developers.
This reduces future hiring risk and dependency on niche platforms.
Lower risk of platform death
Enterprise-backed technologies are less likely to shut down or stagnate.
This protects your app from costly rebuilds in the future.
Cleaner long-term scalability
Well-structured frameworks support growth in users, features, and integrations.
This ensures your app can evolve without major rewrites.
Five years ago, many no-code tools were technical dead ends. In 2026, many are accelerators, not cages.
Decision advice
When choosing any builder or platform:
Check what real code it generates
Make sure the platform produces clean, standard code using modern frameworks.
This protects you from being locked into a black-box system.
Ensure you can export or extend it
Choose tools that allow you to download, customize, and scale your app later.
This keeps long-term ownership and flexibility in your control.
Verify community and enterprise adoption
Look for platforms with active communities and business users.
Strong adoption signals stability, support, and long-term viability.
Your future cost depends on this.
Trend 4: No-Code and Low-Code Are Now Enterprise Tools

This is no longer a “startup experiment.”
Large companies now use low-code platforms to:
Prototype features
Teams can quickly create working versions of app features without full development.
This allows fast testing and feedback before committing resources.
Build internal systems
Low-code platforms enable building CRMs, dashboards, and internal tools.
Businesses streamline operations without hiring full engineering teams.
Launch market tests
Apps and features can be tested with real users rapidly.
This validates demand and identifies improvements before large-scale release.
Automate workflows
Repetitive tasks and processes can be automated using no-code tools.
This boosts efficiency and reduces manual errors.
Reduce software spend
Low-code and AI platforms cut costs on development, maintenance, and external contractors.
Businesses achieve more with smaller budgets.
In consulting projects, I increasingly see marketing, operations, and product teams shipping their own apps — then handing validated products to engineering for scale.
What real builders are shipping
Internal CRMs replacing spreadsheets
Low-code tools allow teams to create structured CRMs that replace manual spreadsheets.
This improves organization, tracking, and efficiency.
Customer portals built by operations teams
Operations teams can build portals for clients without developers.
This enables faster rollout of self-service and support tools.
Loyalty and rewards systems
Apps can implement reward programs quickly using AI or no-code platforms.
This boosts engagement, retention, and repeat usage.
Event, booking, and subscription apps
Businesses can launch scheduling, ticketing, or subscription-based apps rapidly.
Automation handles bookings and payments efficiently.
Niche SaaS products built by solopreneurs
Individual founders can develop specialized SaaS tools using AI-powered platforms.
These reach users and generate revenue without traditional dev teams.
Some of these reach tens of thousands of users before a single traditional developer is hired.
What this changes for buyers
MVP cost drops dramatically
AI and low-code tools reduce development expenses for first versions.
Founders can launch products with minimal upfront investment.
Time-to-market becomes a weapon
Apps can be built and tested in weeks instead of months.
Speed allows you to capture opportunities before competitors react.
Failure becomes affordable
Lower costs and faster builds make experimenting less risky.
You can test ideas without jeopardizing your budget or resources.
Iteration becomes daily instead of quarterly
Rapid prototyping enables frequent updates based on user feedback.
Continuous improvement drives better product-market fit.
The risk is no longer “Can this be built?” It is “Can this attract users?”
Trend 5: Embedded Payments and Super-App Thinking

In 2026, users expect apps to transact.
Subscriptions, wallets, bookings, checkouts, credits, and payouts are becoming default features — not premium extras.
The difference now is accessibility.
What has changed
Payment and financial infrastructure that once took months can now be integrated in days using:
Payment APIs
Integrate payments quickly using ready-made APIs like Stripe or PayPal.
This allows secure transactions without building payment infrastructure from scratch.
Banking-as-a-service platforms
Platforms like Plaid or Stripe provide banking functions as a service.
Founders can add accounts, subscriptions, or payouts without complex development.
AI-assisted setup
AI tools guide integration of payments and financial features.
This reduces errors and speeds up launch for non-technical founders.
Pre-built compliance flows
Regulatory and security requirements come ready-made in modern platforms.
This ensures apps remain compliant without extra legal or dev effort.
I’ve seen fitness apps, tutoring platforms, and niche marketplaces launch full payment systems in under a week.
Common founder mistakes
Avoiding monetization until “later”
Delaying revenue models risks losing early validation and user willingness to pay.
Start monetizing small to test demand quickly.
Redirecting users to external checkout links
Sending users outside the app reduces trust and conversion rates.
Native payment flows create smoother, more reliable experiences.
Over-engineering custom payment systems
Building complex payment systems from scratch wastes time and money.
Pre-built APIs and BaaS platforms handle it faster and more securely.
All three hurt trust and conversion.
Practical guidance
If your app involves transactions:
Make payment native
Embed payment flows directly in your app to improve trust and conversion.
Users complete transactions without leaving the app.
Integrate early
Set up payment systems during the MVP stage.
Early integration helps validate revenue models and avoids costly retrofits later.
Test willingness to pay before scaling features
Confirm that users are willing to pay for your core product first.
This prevents building unnecessary features before revenue is validated.
Revenue validation beats feature validation.
What Most Articles Miss: The New App Success Formula

After working across startups, agencies, and business-led products, I can confidently say:
Technology is no longer the main risk.
The real failure points are:
Solving imaginary problems
Building features users don’t actually need wastes time and resources.
Focus on real pain points validated by research and feedback.
Overbuilding first versions
Adding too many features in the first release slows launch and increases costs.
Start small, solve one problem, and iterate quickly.
Delaying real user exposure
Waiting too long to show your app prevents valuable learning.
Early user interaction uncovers usability issues and validates demand.
Chasing features instead of usage
Prioritizing flashy features over core functionality hurts adoption.
Build what drives real user actions and engagement first.
A 2026-ready validation framework
Day 1–2: Problem proof
Write the exact pain you are solving
Clearly define the specific problem your app addresses.
This ensures your solution targets real user needs.
Identify who feels it weekly
Determine the audience experiencing this pain regularly.
Focusing on active users improves validation and adoption.
List current alternatives they use
Analyze existing solutions your audience relies on.
This helps spot gaps and opportunities for differentiation.
Day 3–4: Market reality
Study negative app reviews in your niche
Analyze what users dislike about similar apps.
This reveals pain points and areas your app can improve.
Map pricing models
Examine how competitors charge and structure payments.
This helps you design competitive and profitable pricing.
Identify where users complain
Spot recurring issues and frustrations in your target audience.
Addressing these gaps can make your app stand out.
Day 5–6: Human validation
Speak to 15–20 target users
Interview potential users to understand their needs and validate your idea.
Direct feedback reduces assumptions and guides design.
Show sketches or Figma
Present early visual prototypes to illustrate your app concept.
This helps users give concrete, actionable feedback.
Ask what they would pay for
Test willingness to pay before building features.
This validates your revenue model and prevents wasted development.
Day 7: Commitment test
Proceed only if at least 5 people:
Want to use it
Ensure at least some users are genuinely interested in your app.
Real demand signals a viable product opportunity.
Understand it without explanation
Users should grasp the core functionality immediately.
Intuitive design reduces confusion and improves early adoption.
Are willing to pay or pre-register
Validate revenue potential by confirming users’ willingness to commit.
Early payment or sign-ups show genuine market interest.
Only then should you open a builder.
How to Build in 2026 Without Wasting Money

Phase 1: Build the smallest useful product
Your first version must:
Solve one painful problem
Focus on addressing a single, real user pain.
Solving one core issue well creates immediate value and adoption.
Work end-to-end
Ensure your MVP functions from start to finish.
Users should complete the core task without gaps or manual workarounds.
Allow real usage
Enable actual users to interact with the app, not just prototypes.
Real usage uncovers practical issues and validates functionality.
Collect feedback
Gather input from early users to guide improvements.
Feedback helps refine features and prioritize next steps effectively.
Ignore:
- Perfect design
- Feature lists
- Multi-platform launches
- Complex onboarding
Phase 2: Ship in 5–8 weeks
This is now realistic for non-technical founders.
Your MVP should include:
Login
Provide secure authentication for users to access the app.
This ensures personalized experiences and protects data.
One core workflow
Focus on the main action users need to complete.
A single streamlined workflow increases usability and adoption.
Basic admin control
Include essential admin tools to manage users, content, and settings.
This keeps operations simple yet effective.
Analytics
Track user behavior and app performance.
Insights guide improvements and validate product decisions.
Payments (if applicable)
Integrate native payment systems for transactions or subscriptions.
This enables monetization without friction.
Anything beyond this is risk.
Phase 3: Let users shape the roadmap
Only build:
What blocks usage
Identify obstacles preventing users from completing tasks.
Removing these friction points ensures your app is functional and user-friendly.
What increases retention
Focus on features or experiences that keep users returning.
Engagement loops and value-driven interactions improve long-term adoption.
What increases revenue
Prioritize elements that directly generate income, like subscriptions or in-app purchases.
This ensures your app grows sustainably.
Delete everything else.
New Sections Competitors Rarely Talk About

The Hidden Cost Trend: AI Infrastructure Planning
As AI becomes core, many apps fail financially because:
Every action hits a paid API
Relying on cloud APIs for every feature can quickly escalate costs.
Optimizing which tasks actually need API calls saves money and improves scalability.
Models are used where logic is enough
Using AI for simple tasks increases complexity and expenses unnecessarily.
Apply AI only when it truly adds value over standard logic.
No on-device processing exists
Processing everything in the cloud adds latency and privacy risks.
Leveraging on-device computation improves speed, reliability, and data security.
Questions every builder should ask:
Founders must now design cost-aware architectures.
What can run locally?
Determine which tasks can be processed on-device instead of the cloud.
Local processing saves costs, improves speed, and protects user data.
What truly needs AI?
Identify features that genuinely benefit from AI instead of using it everywhere.
Focus AI only on tasks that add real value to the app experience.
How does the cost scale with users?
Understand how cloud or AI usage grows as your user base increases.
Planning cost scaling ensures your app remains profitable as it expands.
This will separate profitable apps from impressive but unsustainable ones.
The Talent Shift: Product Operators Beat Engineers

The most valuable people in 2026 app teams are:
User researchers
Study and understand user behavior, needs, and pain points.
Their insights guide app design and feature priorities.
Workflow designers
Create efficient, intuitive processes within apps.
They ensure users can complete tasks smoothly and without friction.
Growth testers
Experiment with features, campaigns, and UX to optimize user acquisition and retention.
Their work drives measurable growth.
Monetization strategists
Design revenue models, pricing, and in-app monetization.
They ensure apps generate sustainable income while delighting users.
Not because engineers are less important — but because building is no longer the bottleneck. Understanding what to build is.
Conclusion
We are in a rare phase where:
- Tools are powerful
- Competition is still adjusting
- Costs are historically low
- Speed advantages are massive
In every fast platform shift I’ve witnessed — from websites to social media to ecommerce — the biggest winners were early builders who shipped before they felt ready.
The same pattern is playing out in mobile apps right now.
You no longer need:
- A technical co-founder
- Large budgets
- Long development cycles
You need:
- A real problem
- Clear thinking
- Fast validation
- The courage to release imperfect work
In 2026, mobile app Development success will belong to those who build early, test often, and let users — not assumptions — guide every decision.
FAQs: Mobile App Development Trends You Can’t Ignore
Not at the MVP stage for most apps. AI and low-code tools now let founders validate and launch before investing in full development teams.
Costs are much lower for first versions using AI-first tools. Businesses now invest small amounts to validate before scaling budgets.
Yes, when built on modern frameworks with proper hosting and security. Most teams upgrade architecture as users and traffic grow.
Marketplaces, subscription apps, internal tools, fitness, education, and fintech-enabled platforms see the biggest advantages.
Building before validating demand. In 2026, speed to real users matters more than feature-heavy development.
About the Author
Paras Dabhi
VerifiedFull-Stack Developer (Python/Django, React, Node.js) · Stellar Code System
Hi, I’m Paras Dabhi. I build scalable web applications and SaaS products with Django REST, React/Next.js, and Node.js. I focus on clean architecture, performance, and production-ready delivery with modern UI/UX.

Paras Dabhi
Stellar Code System
Building scalable CRM & SaaS products
Clean architecture · Performance · UI/UX